Most cited
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Most cited
From articles published in Perspectives on Integrative Medicine during the past two years (2022 ~ ).
Review Articles
- Clinical Research on Pharmacopuncture in Korea: A Scoping Review
- Me-riong Kim, Seong Min Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):8-23. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.003
- 2,031 View
- 64 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- This scoping review was performed as an update on the effects and safety of pharmacopuncture clinical research for the treatment of multiple indications in Korea. Nine electronic databases were searched to identify comparative clinical studies and clinical practice guidelines on Korean pharmacopuncture from inception to December 31, 2022. In vivo and in vitro studies, and case reports were excluded. There were 226 studies identified, including randomized controlled trials, retrospective comparison observational studies, and single-subject crossover designs, of which 17 focused on clinical safety profiles. Most studies pertained to rehabilitation medicine, especially for musculoskeletal (n = 129) and nervous system disorders (n = 35). The evidence supported treatment of neoplasms, obesity, and stroke sequelae. Adverse events of pharmacopuncture were mostly mild and temporary, and occurred more frequently with bee venom compared with herb-derived solutions. Thirty-five clinical practice guidelines including recommendations on pharmacopuncture were included. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first scoping review of clinical pharmacopuncture use in Korea, and our findings support its use in clinical practice and research. Considering the diverse clinical applications of pharmacopuncture, additional pragmatic trials are required to further strengthen the evidence base and develop standard research methodology in Korean medicine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of integrative Korean medicine treatment on symptomatic lumbar facet joint cysts: A case series
Hee-seung Choi, Yoon Jae Lee, Dae-Hyun Hahm, Hyangsook Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
EXPLORE.2024; 20(1): 130. CrossRef - Long-Term Follow-Up of Inpatients with Rotator Cuff Tear Who Received Integrative Korean Medicine Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis and Questionnaire Survey
Dong-Hwi Yoo, Jae-Yong Choi, Sang-Gun Lee, Ki-Won Choi, Han-Bin Park, Ho Kim, Hyunwoo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Doori Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Kyoung Sun Park, In-Hyuk Ha
EXPLORE.2024; 20(2): 212. CrossRef - Long-term follow-up of inpatients with meniscus tears who received integrative Korean medicine treatment: A retrospective analysis and follow-up survey
June Haeng Lee, Jin Young Song, Kyoung Sun Park, Jinho Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Yoon Jae Lee
Medicine.2024; 103(6): e36917. CrossRef - Effectiveness of lumbar motion style acupuncture treatment on inpatients with acute low back pain: A pragmatic, randomized controlled trial
Oh-Bin Kwon, Dong Wook Hwang, Dong-Hyeob Kang, Sang-Joon Yoo, Do-Hoon Lee, Minjin Kwon, Seon-Woo Jang, Hyun-Woo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Kyong Sun Park, Eun-San Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Doori Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2024; 82: 103035. CrossRef - Survey on the current usage of ultrasound-guided procedures in Korean Medicine Clinics and Hospitals
Ju Yeon Kim, Jung Min Yun, Sook-Hyun Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Dong Kun Ko, In Heo, Woo-Chul Shin, Jae-Heung Cho, Byung-Kwan Seo, In-Hyuk Ha
Medicine.2024; 103(14): e37659. CrossRef - A Pragmatic Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effectiveness and Safety of Pharmacopuncture for Chronic Lower Back Pain
Kyoung Sun Park, Changnyun Kim, Joo Won Kim, Sang‐Don Kim, Jee Young Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Jinho Lee, Min Ji Kim, Young Eun Choi, Changsop Yang, Chang-Hyun Han, In-Hyuk Ha
Journal of Pain Research.2023; Volume 16: 2697. CrossRef - Domestic Clinical Research Trends of Shinbaro Pharmacopuncture: Scoping Review
Yeongmin Kim, Yunhee Han, Seungkwan Choi, Jungho Jo, Byeonghyeon Jeon, Hyeonjun Woo, Wonbae Ha, Junghan Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2023; 33(4): 125. CrossRef
- The effect of integrative Korean medicine treatment on symptomatic lumbar facet joint cysts: A case series
- A Review of Major Secondary Data Resources Used for Research in Traditional Korean Medicine
- Chunhoo Cheon, Bo-Hyoung Jang, Seong-Gyu Ko
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):77-85. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.002
- 1,001 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Research in health care using secondary data is steadily increasing worldwide. In this study, secondary healthcare data was reviewed, so that the information can potentially be used for Korean medicine research. The characteristics of the data, including the variables related to Korean medicine and the method of obtaining data, were summarized. The Korean medicine variables were extracted from the Korean Medicine Utilization Survey, Korea Health Panel, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Medical Service Experience Survey, and the health insurance claims data. Except for health insurance claims data, the data was obtained through relatively simple procedures. There were differences in the characteristics of each secondary data and the extent to which it was used in Korean medicine research. Many Korean medicine studies using secondary data will be conducted in the future and researchers must understand the characteristics of the data and analyze it appropriately.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-world data analysis on effectiveness of integrative therapies: A practical guide to study design and data analysis using healthcare databases
Ye-Seul Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
Integrative Medicine Research.2023; 12(4): 101000. CrossRef - Trends in the treatment of fibromyalgia in South Korea between 2011 and 2018: a retrospective analysis of cross-sectional health insurance data
Jin-Sil Yu, Eun-San Kim, Kyoung Sun Park, Yoon Jae Lee, Yeon Cheol Park, Dongwoo Nam, Eun-Jung Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
BMJ Open.2023; 13(12): e071735. CrossRef
- Real-world data analysis on effectiveness of integrative therapies: A practical guide to study design and data analysis using healthcare databases
- A Scoping Review of Clinical Research on Motion Style Acupuncture Treatment
- Doori Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):65-76. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.001
- 1,382 View
- 39 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- This scoping review was conducted to examine the concept of Motion style acupuncture treatment (MSAT), use in clinical practice, its effectiveness, and safety. A literature review of clinical study treatment methods combining acupuncture and movement therapy was performed using PubMed. Of 2,096 studies retrieved, 22 were included in this review. There were 12 randomized controlled trials, and all 22 studies were published in China and Korea, mostly, within the last 3 years. There were five studies concerning local acupoints and 17 studies regarding needling at distal acupoints, and the level of risk of the procedure was “high” in eight studies and “moderate” in 14 studies. The study participants were patients with musculoskeletal pain, and many studies reported significant improvements in pain and functional disability outcomes following treatment using MSAT. For conclusion, MSAT refers to a treatment method in which a patient performs active/passive movements under the supervision of a physician with the acupuncture needle retained at the insertion site. However, there are a limited number of MSAT studies, and various treatment types and related terms are mixed. Further studies, classification of the types of MSAT using a well-established classification system, and a clearer definition of the MSAT concept are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of lumbar motion style acupuncture treatment on inpatients with acute low back pain: A pragmatic, randomized controlled trial
Oh-Bin Kwon, Dong Wook Hwang, Dong-Hyeob Kang, Sang-Joon Yoo, Do-Hoon Lee, Minjin Kwon, Seon-Woo Jang, Hyun-Woo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Kyong Sun Park, Eun-San Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Doori Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2024; 82: 103035. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Safety of Progressive Loading–Motion Style Acupuncture Treatment for Acute Low Back Pain after Traffic Accidents: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Seung-Yoon Hwangbo, Young-Jun Kim, Dong Guk Shin, Sang-Joon An, Hyunjin Choi, Yeonsun Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Ju Yeon Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
Healthcare.2023; 11(22): 2939. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of lumbar motion style acupuncture treatment on inpatients with acute low back pain: A pragmatic, randomized controlled trial
- Trends in the Development of Sham Acupuncture-Related Technologies Focused on Patents Applied for in South Korea
- Sung Min Lim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):36-41. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.005
- 1,347 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 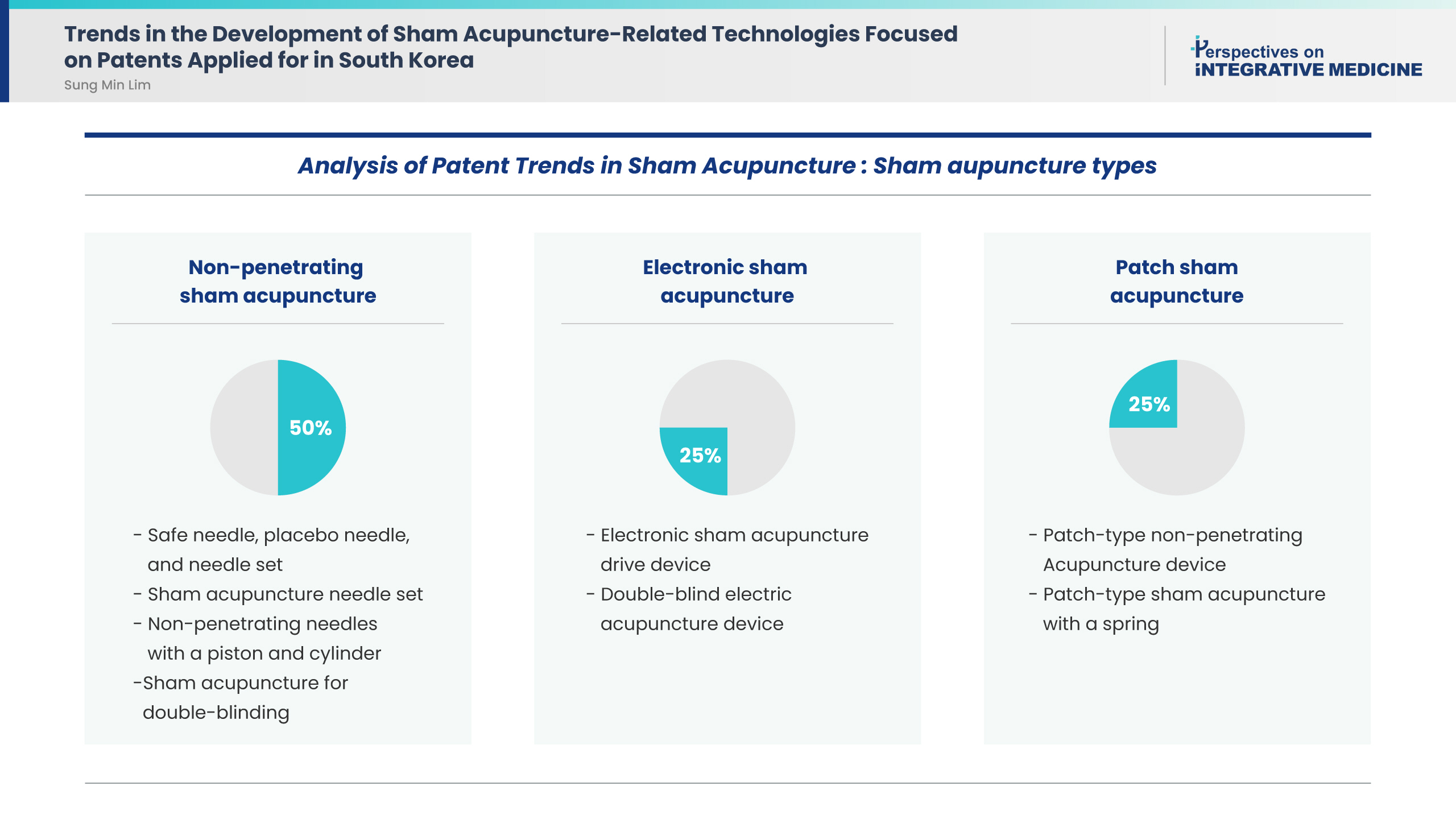
- Background
This study aimed to analyze the trends in Korean patents for sham acupuncture.
Methods
The electronic database of the Korea Intellectual Property Rights Information Service was searched for Korean patents for sham acupuncture from inception till September 2020. Patents, which were not related to sham acupuncture, were excluded. The applicant, application date, International Patent Classification, and technological content of sham acupuncture were analyzed.
Results
This study included eight patents. Application analysis identified the following sham acupuncture types: four (50%), two (25%), and two (25%) patents were for non-penetrating sham acupuncture, electronic sham acupuncture, and patch sham acupuncture, respectively. All patents aimed to use sham acupuncture as a control for rigorous double-blind clinical trials to verify the efficacy of real acupuncture treatment.
Conclusion
The present findings suggest that technological advances were focused on developing various types of sham acupuncture methods for double-blind studies. Further large-scale studies using rigorous designs are needed to investigate new sham acupuncture applications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
Editorial
- Integration of Acupuncture into UK Healthcare - A NICE Perspective: Why is Acupuncture Now Recommended for Chronic Pain but not for Back Pain or Osteoarthritis
- Mike Cummings
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):3-7. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.002
- 1,799 View
- 35 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In April 2021, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) published a guideline on chronic pain (NG193) with a recommendation to consider a single course of acupuncture treatment in patients with chronic primary pain. This positive recommendation came after the NICE guideline on low back pain and sciatica (NG59) announced in November 2016, that acupuncture treatment did not work for back pain, having previously recommended it in 2009 (CG88). This article attempts to explain this apparent contradiction in recommendations by tracing the history of acupuncture debates in the NICE guidelines over the last 2 decades.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of Key Research and Engagement in 2022
John McDonald, Sandro Graca, Claudia Citkovitz, Lisa Taylor-Swanson
Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine.2023; 29(8): 455. CrossRef
- A Review of Key Research and Engagement in 2022
Review Articles
- Effects of Acupuncture on Neuropathic Pain: Mechanisms in Animal Models
- Jae-Hwan Jang, Hi-Joon Park
- Perspect Integr Med. 2022;1(1):17-20. Published online September 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2022.09.004
- 1,136 View
- 32 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Neuropathic pain is a chronic condition/disease characterized by mechanical and thermal pain. Neuropathic pain can have various comorbidities such as depression, anxiety disorders and cognitive impairment, and as a result, can have a detrimental effect on quality of life. Pain and comorbid symptoms are often complicated, intertwined, affect each other, and present difficulties in treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to improve both pain and comorbid symptoms to treat neuropathic pain. Acupuncture is effective in treating not only pain but other conditions/diseases such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment. Recently, acupuncture was reported to be effective in improving comorbid symptoms in patients with chronic pain. This review aimed to describe the mechanisms of action of acupuncture on the brain with respect to the improvement of comorbid symptoms that appeared in animal models of chronic neuropathic pain. Comorbidity-pain studies were comprehensively reviewed. Both manual acupuncture and electroacupuncture improved not only mechanical and thermal pain but also comorbid symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment in patients with chronic neuropathic pain. The results of this review suggest that comorbid symptoms can be improved through various mechanisms, including the dopamine system in the brain, glutamate system, inflammation, epigenetic modulation, and mitochondrial function.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long-term follow-up of inpatients with meniscus tears who received integrative Korean medicine treatment: A retrospective analysis and follow-up survey
June Haeng Lee, Jin Young Song, Kyoung Sun Park, Jinho Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Yoon Jae Lee
Medicine.2024; 103(6): e36917. CrossRef
- Long-term follow-up of inpatients with meniscus tears who received integrative Korean medicine treatment: A retrospective analysis and follow-up survey
- Shoulder Pain and the Potential Role of Acupuncture: A Narrative Review of Clinical Practice and Treatment Guidelines
- Stephen Birch, Myeong Soo Lee, Tae-Hun Kim, Terje Alraek
- Perspect Integr Med. 2022;1(1):3-9. Published online September 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2022.09.002
- 3,552 View
- 100 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - The potential use of acupuncture for shoulder pain of various etiologies and whether clinicians make recommendations about the use of acupuncture was examined. Shoulder pain is a common clinical problem. What is the level of evidence and how often is acupuncture recommended for shoulder pain? A manual and database (PubMed) search of review articles of related clinical trials and guidelines was performed. The evidence for effectiveness of acupuncture treatment of different types of shoulder pain was weak. However, there are some studies, with a weak to moderate level of evidence, on shoulder pain (across nine subtypes of shoulder pain). Acupuncture is safe and may be a cost-effective treatment for shoulder pain. There were 131 statements recommending the use of acupuncture for shoulder pain across 12 subtypes of shoulder pain. The most common statements were for non-specific ‘shoulder pain.’ There were 11 statements against the use of acupuncture for shoulder pain and three subtypes of shoulder pain. The level of evidence in studies of acupuncture treatment for shoulder pain is low, therefore, further research is needed. Recommendations for the use of acupuncture for shoulder pain are increasing but lag behind those for other pain problems such as low back pain.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of Key Research and Engagement in 2022
John McDonald, Sandro Graca, Claudia Citkovitz, Lisa Taylor-Swanson
Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine.2023; 29(8): 455. CrossRef
- A Review of Key Research and Engagement in 2022



 First
First Prev
Prev


