Most download
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Most download
Most-download articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last three month.
Case Report
- Complete Remission of Drug-Induced Acute Dizziness Using Eight Constitution Acupuncture and the Barbecue Maneuver: A Case Report
- Younkuk Choi, Juhee Cho
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):51-56. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.007
- 755 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dizziness, often symptomatic of underlying conditions, presents management challenges especially when dealing with drug-induced vestibular disorders. Complementary therapies like acupuncture, specifically, Eight Constitution Acupuncture (ECA), offers a potential alternative to other management therapies. A 74-year-old female, experiencing sudden dizziness from medication for back pain, underwent a detailed examination, constitutional diagnosis, and targeted acupuncture involving 26 insertions over 4 sessions. The treatment for dizziness, which focused on constitutional differences, integrated ECA and the barbecue maneuver which resulted in significant efficacy. A 50% reduction in the Numeric Rating Scale score from 10 to 5 was observed after the 1st session. Subsequent sessions of ECA combined with the barbecue maneuver significantly reduced symptoms of dizziness and ultimately alleviated symptoms. This case underscored the potential of ECA when combined with the application of the barbecue maneuver in treating drug-induced vestibular disorders and residual benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. The ECA's constitutional approach allows for precise targeting and symptom resolution, and integrating the principles of Traditional Asian Medicine with biological mechanisms. Notably, this is the 1st case report of the efficacy of ECA and the barbecue maneuver in addressing drug-induced vestibular disorders. A holistic approach, considering constitutional differences, can offer insights and tailored solutions to present a promising avenue for patients experiencing such conditions. Rigorous research studies are essential to validate these findings.
Original Article
- Acupuncture Needles and the Risk of Lymphedema After Breast Cancer Surgery: A Retrospective National Cohort Study
- Ye-Seul Lee, Yucheol Lim, Jiyoon Yeo
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):29-36. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.004
- 596 View
- 23 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Background
Controversies remain over the impact of using needles on breast cancer patients after surgery due to risk of breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL). While recent literature suggests that vascular access during the postsurgical stage does not affect the risk of BCRL, the impact of acupuncture on the risk of BCRL during the postsurgical stage has not been studied.
Methods
This study included 35,153 patients from 2011 to 2013 who were newly diagnosed with breast cancer in a population-based cohort from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database. All patients received breast surgery, and the treatment group received acupuncture for more than 3 sessions in the 3-6 months post-surgery. The control group did not receive acupuncture. The incidence rate ratio, Kaplan-Meier curve, and Cox proportional hazards models were used to compare the risk of BCRL, and death between groups.
Results
About 5.8% of the study population received acupuncture during the 3-6 months post-surgery treatment window. After propensity score matching, the acupuncture treatment group did not show an increased risk of BCRL (IRR 1.017, 95% CI 0.868-1.193; unadjusted HR 1.018, 95% CI 0.868-1.193). This risk was robust in all multivariate Cox proportional hazards models.
Conclusion
An association of BCRL with acupuncture was not observed. Patients who received acupuncture to manage symptoms such as pain during the 3-6 months postsurgical stage did not have a higher risk of developing BCRL. Breast cancer patients who seek acupuncture to alleviate post-surgery symptoms such as pain, can receive acupuncture without concerns for potential risk of BCRL.
Review Articles
- Effectiveness and Safety of Low-Level Laser Treatment for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sang Jun Lee, Seung Jin Noh, Jeong Rock Kim, Kyung Bok Park, Sae-rom Jeon, Yejin Hong, Dongwoo Nam
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):155-163. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.003
- 1,295 View
- 44 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Background
Low-level laser treatment (LLLT) is used to treat low back pain (LBP) however, its effects on lumbar disc herniation (LDH) remain unclear. The safety and effectiveness of LLLT for LDH was determined using a systematic review of randomized clinical trials.
Methods
Studies on LLLT in adults with LDH were identified from 12 worldwide databases. A risk of bias assessment and a meta-analysis with categorization according to the type of control used (inactive, active, or add-on) was performed. The quality of evidence was assessed using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation.
Results
The quantitative analyses included five studies. LLLT was significantly more effective at treating LDH [leg pain visual analog scale (VAS) mean difference (MD): -1.90, 95% confidence interval (CI): -2.01, -1.80, I2 80%; LBP VAS MD: -0.79, 95% CI: -0.87, -0.71, I2 80%] than inactive controls (placebo or sham). The quality of the evidence ranged from “low” to “very low.” As an add-on to usual care, LLLT significantly improved pain intensity and disability compared with usual care (leg pain VAS MD: -2.52, 95% CI: -2.65, -2.40, I2 97%; LBP VAS MD: -1.47, 95% CI: -1.58, -1.36; Oswestry Disability Index MD: -4.10, 95% CI: -4.55, -3.65, I2 6%). However, the quality of the evidence ranged from “moderate” to “low.”
Conclusion
LLLT significantly improved outcomes compared with the inactive controls, but was not more effective than usual care for LDH. In combination with usual care, LLLT was significantly more effective than usual care alone highlighting the potential of LLLT.
- Shoulder Pain and the Potential Role of Acupuncture: A Narrative Review of Clinical Practice and Treatment Guidelines
- Stephen Birch, Myeong Soo Lee, Tae-Hun Kim, Terje Alraek
- Perspect Integr Med. 2022;1(1):3-9. Published online September 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2022.09.002
- 3,550 View
- 100 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - The potential use of acupuncture for shoulder pain of various etiologies and whether clinicians make recommendations about the use of acupuncture was examined. Shoulder pain is a common clinical problem. What is the level of evidence and how often is acupuncture recommended for shoulder pain? A manual and database (PubMed) search of review articles of related clinical trials and guidelines was performed. The evidence for effectiveness of acupuncture treatment of different types of shoulder pain was weak. However, there are some studies, with a weak to moderate level of evidence, on shoulder pain (across nine subtypes of shoulder pain). Acupuncture is safe and may be a cost-effective treatment for shoulder pain. There were 131 statements recommending the use of acupuncture for shoulder pain across 12 subtypes of shoulder pain. The most common statements were for non-specific ‘shoulder pain.’ There were 11 statements against the use of acupuncture for shoulder pain and three subtypes of shoulder pain. The level of evidence in studies of acupuncture treatment for shoulder pain is low, therefore, further research is needed. Recommendations for the use of acupuncture for shoulder pain are increasing but lag behind those for other pain problems such as low back pain.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of Key Research and Engagement in 2022
John McDonald, Sandro Graca, Claudia Citkovitz, Lisa Taylor-Swanson
Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine.2023; 29(8): 455. CrossRef
- A Review of Key Research and Engagement in 2022
Original Article
- Contributing Factors in the Decision to Study Korean Medicine and Satisfaction with the College Experience: A Quantitative Nationwide Study
- HyunSeok Kim, Hyunho Kim, Joohyun Lee, Hwimun Kim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):173-181. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.005
- 708 View
- 29 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Background
The practice of Korean medicine (KM) taught at KM colleges has equal legal rights and responsibilities as Western medicine in South Korea. To date, no research has been conducted on the factors which influence college students in their choice to study KM and satisfaction with the course.
Methods
Content validity and face validity tests were conducted while developing the questionnaires. Research was conducted amongst all KM colleges in South Korea and of the 744 premedical KM 2nd year students, 420 participated. Analysis was performed on how much the mean values changed between the items and sub-items. Factors were also correlated with the students’ satisfaction and willingness to reenter KM colleges.
Results
The means of stable incumbency items were the highest of all the items, while items concerning experience of chronic disease had the lowest mean values. For enrollment, the latent value that most questionnaire items were changed positively by was interest in KM. Items related to students’ choice or KM doctor status were closely tied to students’ current satisfaction with their choice to enroll at a KM college, rather than their college entrance examination scores.
Conclusion
Identifying which factors are considered before entering KM college and during the course can help students to be more satisfied with their academic progress. To satisfy the KM students, educators should focus on providing both qualified clinical training and guidance to enter diverse career fields. This study highlights factors that can be applied to college curriculum or subject teaching.
Editorial
- A Pilot Trial of Integrative Medicine for Stroke Rehabilitation: Expert Recommendations for the Development and Sustainability of Integrative Medicine
- Chihyoung Son, Go-Eun Lee, Joo-Hee Seo, Inae Youn, Jin-Won Kim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):1-6. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.001
- 649 View
- 17 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Background
Strategies towards development and sustainability of integrative treatment in stroke rehabilitation medicine are needed. National expert recommendations based on the implementation of Integrative Medicine (IM) in stroke rehabilitation and IM outcomes would be invaluable.
Methods
A pilot study was performed and the effectiveness of combining Korean traditional medicine and Western conventional medicine in post-stroke patients (ischemic stroke n = 15 and hemorrhagic stroke n = 4) was evaluated, and recommendations were developed through consensus with physicians in national centers of rehabilitative medicine. Outcome measures [Korean Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI), Korean Mini Mental State Examination (K-MMSE), Modified Rankin Scale (mRS), and EuroQol 5-dimension 5-level (EQ-5D-5L) assessment were used at baseline, 4, 8 (K-MBI, K-MMSE, mRS, and EQ-5D-5L) and 12 weeks post treatment (EQ-5D-5L and mRS).
Results
Improvements were observed in functional and cognitive abilities at 8 weeks (K-MBI score p = 0.0062; K-MMSE score p = 0.046). Quality of life improvements (EQ-5D-5L) were observed but were not statistically significant. The disability assessment (mRS) indicated a gradual improvement from baseline to 12 weeks. No adverse events were reported. For effective, patient-centered IM treatment: (1) build a strong evidence base for IM as compared with Western medicine alone or traditional medicine alone; (2) active expert collaboration; (3) IM promotion in public medical institutions; and (4) continued government support.
Conclusion
Functional and cognitive abilities of stroke patients statistically significantly improved following 8 weeks of IM treatment. Strategies have been suggested towards the development and sustainability of IM treatment in stroke rehabilitation medicine.
Letter
- Treatment Recommendations in Korea for Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: The Evidence for Acupuncture Treatment in Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients Should be Re-evaluated
- Tae-Hun Kim, Myeong Soo Lee, Hyangsook Lee, Stephen Birch, Terje Alraek
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):61-62. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.009
- 474 View
- 11 Download
Review Articles
- A Modern Interpretation of Cold-Heat Pattern in Traditional Medicine with a Focus on Thermo-Regulation
- Younggwang Kim, Jee Young Lee, Joongho Lee, Sanghun Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):18-28. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.003
- 444 View
- 15 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 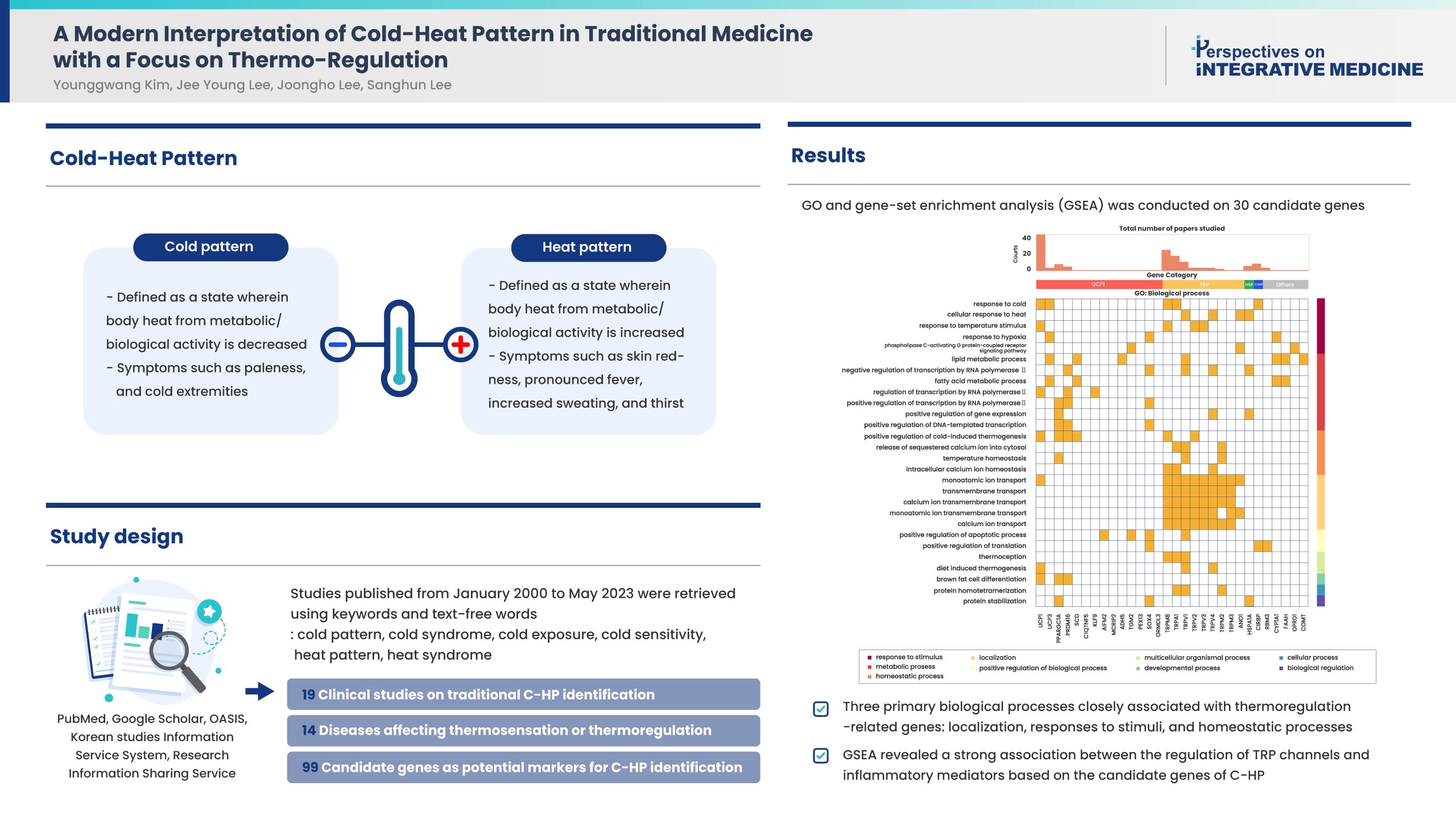
- Cold-heat patterns (C-HPs) in Traditional East Asian Medicine are essential for individually diagnosing and treating patients. However, the concept of C-HPs and their biological mechanisms (thermoregulation) remains unclear. C-HPs studies published between January 2000 and May 2023 were retrieved from 5 databases (PubMed, Google Scholar, OASIS, Korean studies Information Service System, and Research Information Sharing Service). Among the 8,373 articles screened, 132 were included in the review and categorized. Nineteen articles were clinical studies related to traditional concept of C-HP identification, 14 studies investigated diseases affecting thermosensation or thermoregulation, and 99 studies identified candidate genes as potential markers for C-HP identification. Further analysis, including gene ontology, and gene set enrichment analysis of the candidate genes, revealed 3 primary biological processes closely associated with thermoregulation-related genes, including localization, responses to stimuli, and homeostatic processes. Notably there was a significant association between the candidate genes and inflammatory mediator regulation of transient receptor potential channels (p < 0.001). A significant association between C-HPs and inflammation-related pathways across thermosensation-related and thermoregulation-related clinical and preclinical studies was observed, suggesting that the traditional concept of C-HPs should be studied further from an immunological perspective.
- Characteristics and Quality of Traditional Chinese Therapies and Integrative Medicine Clinical Practice Guidelines for Musculoskeletal Disorders Published in Mainland China
- Xue-Feng Wang, Jing-Ling Zuo, Lin-Jian Li, Lan-Dan Xu, Xiao-Zhong Liu, Si-Si Ma, Jian-Ping Liu
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):7-17. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.002
- 584 View
- 15 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 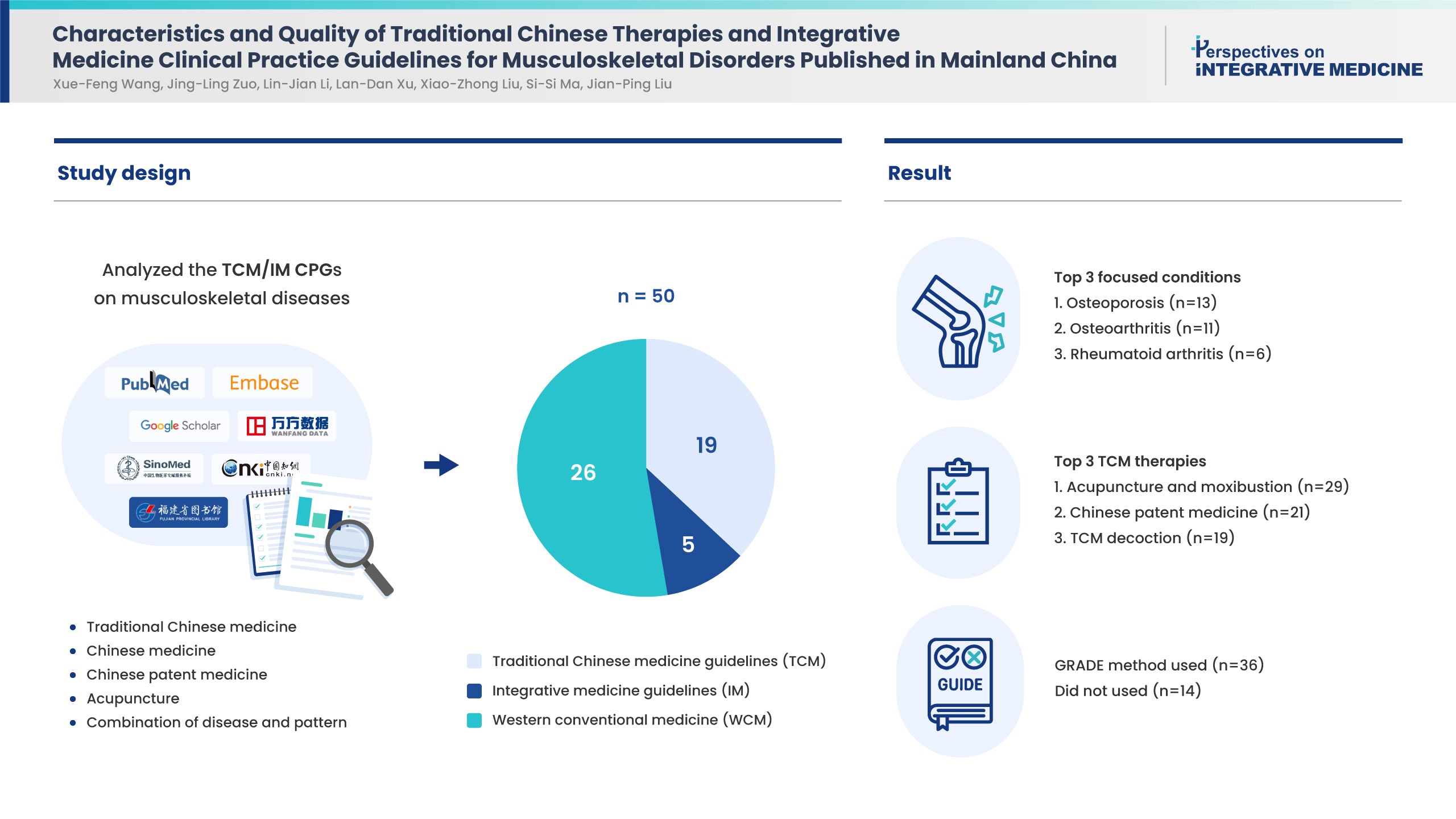
- Background
Musculoskeletal disorders are prevalent in adults. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and integrative medicine (IM) are commonly used treatments which have clinical practice guidelines (CPGs). This study aimed to determine the characteristics and quality of these CPGs.
Methods
CPGs which recommended TCM/IM therapies in musculoskeletal conditions/diseases published in Chinese or English between January 2018 to December 2022 in mainland China were retrieved and analyzed for guideline classification, funding source, conflict of interest, and methodology. Appraisal of Guideline for Research and Evaluation Ⅱ including 6 domains, was applied to assess CPG quality.
Results
Of the 50 CPGs included, there were 19 TCM, 5 IM, and 26 western conventional medicine (WCM) guidelines of which osteoporosis (13, 26%), osteoarthritis (11, 22%) and rheumatoid arthritis (6, 12%) were the most frequent diseases. The TCM therapies recommended by the CPGs successively were acupuncture and moxibustion, Chinese patent medicine, and TCM decoction based on syndrome differentiation. Nearly half of the CPGs reported funding source (52%) and conflict of interest (48%). Thirty-six CPGs used the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations method to present summaries of evidence, the remaining did not report the method. Based on Appraisal of Guideline for Research and Evaluation Ⅱ scores, “clarity of presentation” scored the highest (55%), while “applicability” was the lowest (6%). No CPG was recommended without change, and 23 CPGs were not recommended.
Conclusion
The quality of CPGs for musculoskeletal conditions/diseases in China is generally low. Future CPGs should pay more attention to standardized developing procedures.
Letter
- Tendon Rupture by Acupuncture? Reporting of Not Probable Causality Might Exaggerate Harm of Acupuncture
- Sung-A Kim, Tae-Hun Kim, Jung Won Kang
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):63-64. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.010
- 654 View
- 10 Download
Review Article
- An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews for Chuna (or Tuina) Manual Therapy on Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Doori Kim, Gil Geun Baek, Byung-Cheul Shin
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):142-154. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.002
- 736 View
- 29 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Background
To provide clinicians with reliable evidence an umbrella review of systematic reviews (SRs) on Chuna manual therapy (CMT) for musculoskeletal disorders was performed to synthesize important outcomes.
Methods
There were eight databases (Cochrane, EMBASE, MEDLINE, CNKI, KMBASE, KISS, Scienceon, and OASIS) searched as well as the international database Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews in health and social care until August 2023. SRs of randomized controlled trials involving patients with musculoskeletal conditions, limited to interventions explicitly labeled as “Chuna” or “Tuina” in English, Chinese, or Korean language were retrieved. Two reviewers independently conducted selection and data extraction, and SR quality was assessed using A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews tool (low, medium, or high quality).
Results
This review included 32 SRs, categorized by cervical (n = 4), thoracolumbar (n = 7), upper extremity (n = 5), lower extremity (n = 9), and other musculoskeletal disorders (n = 7). Quality assessments determined that three SRs were of “high” quality, two were “low” quality, and the remaining SRs were of “medium” quality. CMT was consistently reported to demonstrate superior outcomes: an effective rate was observed in 17 of 19 SRs, CMT was effective at reducing pain in 12 of the 16 SRs, and functional outcomes of CMT were observed in 8 of 12 SRs. No serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusion
CMT may be a safe and effective treatment for various musculoskeletal disorders based on the limited number of studies and the low quality of included SRs.
Original Article
- Effects of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy and Photontherapy in Cervicobrachialgia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Bianca dos Santos Bobadilha, Talita Bonato de Almeida, Maria Imaculada de Lima Montebello, Maria da Luz Rosário de Sousa
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):37-44. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.005
- 499 View
- 10 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 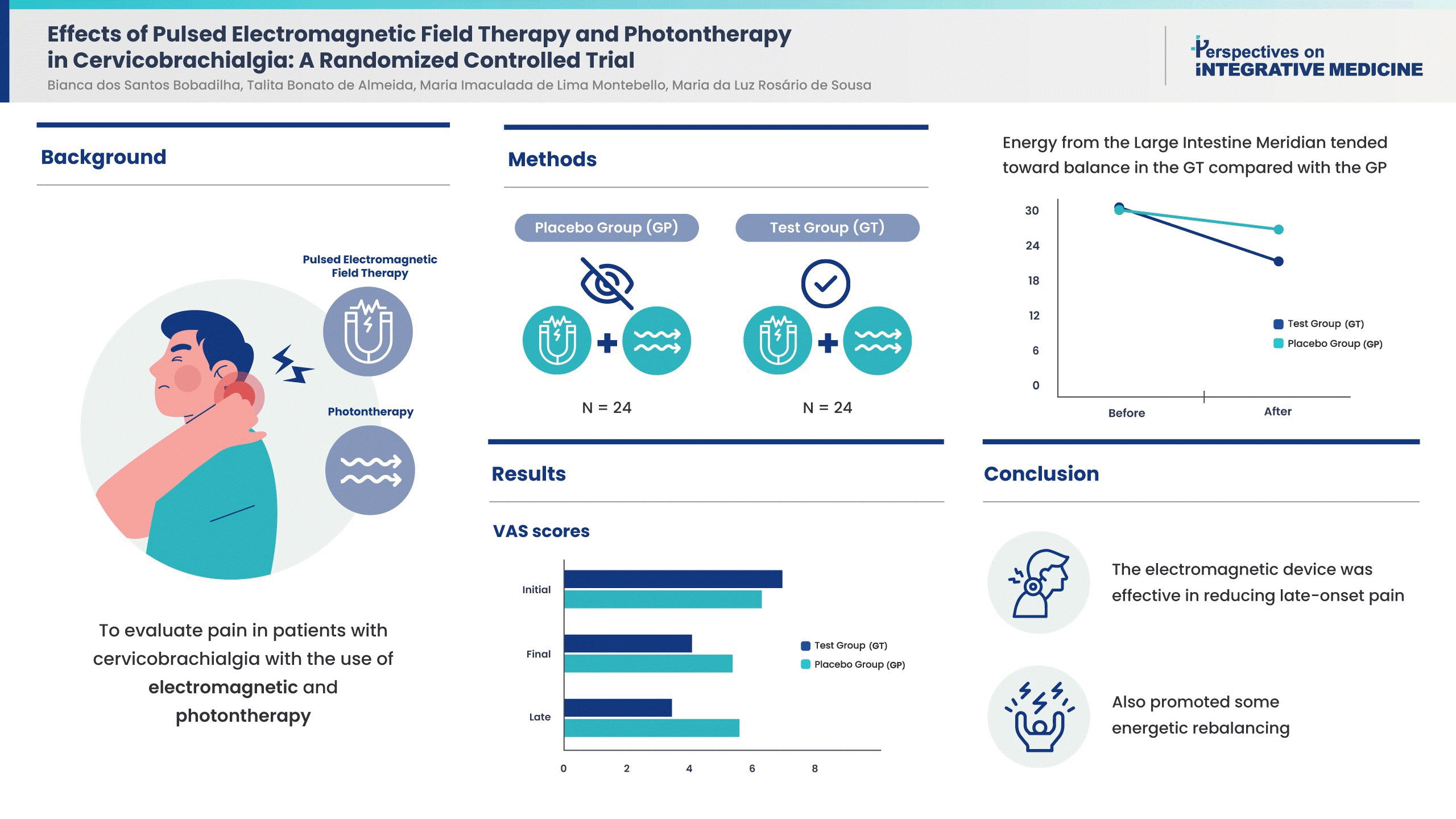
- Background
Cervicobrachialgia is a painful condition commonly treated with medication and physiotherapy. The aim was to evaluate pain following electromagnetic and photontherapy, and examine patient energy profiles.
Methods
There were 48 patients experiencing pain [Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score ≥ 4] who were not receiving medication and physiotherapy and were randomized into Test Group (GT); electromagnetism using a Kenkobio device (intensity = 0.055 mT/frequency = 60 Hz) and photon therapy; a photon therapy blanket, and Placebo Group (GP); the Kenkobio device was turned off and the blanket was not used. Pain was assessed using the VAS, before, immediately after treatment, and the following day. Algometry was also carried out before and after the treatment to understand the pain threshold at bilateral acupoints GB20 and GB21. The energy profile was assessed using Ryodoraku measurements before and after the session.
Results
The GT achieved a greater reduction in pain the following day than GP. Both groups were equal for left GB20 and right GB21 points considering algometry and, after the intervention, a reduction in pain in the GT was noticed only in the left GB20 (CI [95%]: 0.09-0.99, p = 0.019). The average energy level was low and dropped further following treatment. Furthermore, energy from the Large Intestine Meridian tended towards balance in the GT compared with the GP [CI (95%): 0.58-15.75, p = 0.035]. No adverse effects were reported.
Conclusion
The combined use of electromagnetic and photontherapy were effective in reducing pain in patients and promoted energy rebalancing.
Review Article
- A Scoping Review of Clinical Research on Motion Style Acupuncture Treatment
- Doori Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):65-76. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.001
- 1,381 View
- 39 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- This scoping review was conducted to examine the concept of Motion style acupuncture treatment (MSAT), use in clinical practice, its effectiveness, and safety. A literature review of clinical study treatment methods combining acupuncture and movement therapy was performed using PubMed. Of 2,096 studies retrieved, 22 were included in this review. There were 12 randomized controlled trials, and all 22 studies were published in China and Korea, mostly, within the last 3 years. There were five studies concerning local acupoints and 17 studies regarding needling at distal acupoints, and the level of risk of the procedure was “high” in eight studies and “moderate” in 14 studies. The study participants were patients with musculoskeletal pain, and many studies reported significant improvements in pain and functional disability outcomes following treatment using MSAT. For conclusion, MSAT refers to a treatment method in which a patient performs active/passive movements under the supervision of a physician with the acupuncture needle retained at the insertion site. However, there are a limited number of MSAT studies, and various treatment types and related terms are mixed. Further studies, classification of the types of MSAT using a well-established classification system, and a clearer definition of the MSAT concept are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of lumbar motion style acupuncture treatment on inpatients with acute low back pain: A pragmatic, randomized controlled trial
Oh-Bin Kwon, Dong Wook Hwang, Dong-Hyeob Kang, Sang-Joon Yoo, Do-Hoon Lee, Minjin Kwon, Seon-Woo Jang, Hyun-Woo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Kyong Sun Park, Eun-San Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Doori Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2024; 82: 103035. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Safety of Progressive Loading–Motion Style Acupuncture Treatment for Acute Low Back Pain after Traffic Accidents: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Seung-Yoon Hwangbo, Young-Jun Kim, Dong Guk Shin, Sang-Joon An, Hyunjin Choi, Yeonsun Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Ju Yeon Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
Healthcare.2023; 11(22): 2939. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of lumbar motion style acupuncture treatment on inpatients with acute low back pain: A pragmatic, randomized controlled trial
Original Article
- A Survey of the Clinical Practice of Korean Medicine for Smoking Cessation in Public Health Centers: A Web-Based Survey of Public Health Doctors of Korean Medicine
- Gyoungeun Park, Jeong-Hyun Moon, Eun-Jung Kim, Byung-Kwan Seo, Yong-Hyeon Baek, Won-Suk Sung
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):45-50. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.006
- 515 View
- 9 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Background
In South Korea, public health centers provide smoking cessation (SC) treatments including behavioral therapy and nicotine replacement treatment. Also, public health doctors of Korean medicine (PHDKMs) are providing Korean Medicine (KM) treatments. Several studies have reported the clinical usefulness of KM treatment, but in this study, the opinion of PHDKMs was explored to examine the current KM treatments for SC.
Methods
A web-based survey (Moaform) of the treatment for SC by PHDKMs consisted of 5 main sections including clinical practice status, SC participants, KM treatments for SC, progress and prognosis, and perception of KM. The survey was emailed twice to 621 PHDKMs on April 6 to 20, 2022. The frequencies and percentages of each question were calculated.
Results
There were 28 PHDKMs who participated in the survey. Among them, over 90% of PHDKMs had treated ≤ 10 SC participants, and about 10% of PHDKMs had treated 11-20 participants. The abstinence rate was 56.8% with an average 63.2% level of satisfaction in the treatment. Typically used, and recognized as important KM treatments, were auricular acupuncture, acupuncture, education, and herbal medicine. While auricular acupuncture and education were perceived as convenient KM treatment, PHDKMs thought that SC could not be achieved with KM treatment alone and needed be combined with other treatments.
Conclusion
This survey showed the effectiveness of KM treatments with withdrawal symptoms, and treatment satisfaction of SC participants. Respondents also thought that KM treatment combined with other treatments is more effective than KM monotherapy. Based on this small study, further research would be needed.
Review Article
- Clinical Research on Pharmacopuncture in Korea: A Scoping Review
- Me-riong Kim, Seong Min Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):8-23. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.003
- 2,030 View
- 64 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- This scoping review was performed as an update on the effects and safety of pharmacopuncture clinical research for the treatment of multiple indications in Korea. Nine electronic databases were searched to identify comparative clinical studies and clinical practice guidelines on Korean pharmacopuncture from inception to December 31, 2022. In vivo and in vitro studies, and case reports were excluded. There were 226 studies identified, including randomized controlled trials, retrospective comparison observational studies, and single-subject crossover designs, of which 17 focused on clinical safety profiles. Most studies pertained to rehabilitation medicine, especially for musculoskeletal (n = 129) and nervous system disorders (n = 35). The evidence supported treatment of neoplasms, obesity, and stroke sequelae. Adverse events of pharmacopuncture were mostly mild and temporary, and occurred more frequently with bee venom compared with herb-derived solutions. Thirty-five clinical practice guidelines including recommendations on pharmacopuncture were included. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first scoping review of clinical pharmacopuncture use in Korea, and our findings support its use in clinical practice and research. Considering the diverse clinical applications of pharmacopuncture, additional pragmatic trials are required to further strengthen the evidence base and develop standard research methodology in Korean medicine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of integrative Korean medicine treatment on symptomatic lumbar facet joint cysts: A case series
Hee-seung Choi, Yoon Jae Lee, Dae-Hyun Hahm, Hyangsook Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
EXPLORE.2024; 20(1): 130. CrossRef - Long-Term Follow-Up of Inpatients with Rotator Cuff Tear Who Received Integrative Korean Medicine Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis and Questionnaire Survey
Dong-Hwi Yoo, Jae-Yong Choi, Sang-Gun Lee, Ki-Won Choi, Han-Bin Park, Ho Kim, Hyunwoo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Doori Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Kyoung Sun Park, In-Hyuk Ha
EXPLORE.2024; 20(2): 212. CrossRef - Long-term follow-up of inpatients with meniscus tears who received integrative Korean medicine treatment: A retrospective analysis and follow-up survey
June Haeng Lee, Jin Young Song, Kyoung Sun Park, Jinho Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Yoon Jae Lee
Medicine.2024; 103(6): e36917. CrossRef - Effectiveness of lumbar motion style acupuncture treatment on inpatients with acute low back pain: A pragmatic, randomized controlled trial
Oh-Bin Kwon, Dong Wook Hwang, Dong-Hyeob Kang, Sang-Joon Yoo, Do-Hoon Lee, Minjin Kwon, Seon-Woo Jang, Hyun-Woo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Kyong Sun Park, Eun-San Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Doori Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2024; 82: 103035. CrossRef - Survey on the current usage of ultrasound-guided procedures in Korean Medicine Clinics and Hospitals
Ju Yeon Kim, Jung Min Yun, Sook-Hyun Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Dong Kun Ko, In Heo, Woo-Chul Shin, Jae-Heung Cho, Byung-Kwan Seo, In-Hyuk Ha
Medicine.2024; 103(14): e37659. CrossRef - A Pragmatic Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effectiveness and Safety of Pharmacopuncture for Chronic Lower Back Pain
Kyoung Sun Park, Changnyun Kim, Joo Won Kim, Sang‐Don Kim, Jee Young Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Jinho Lee, Min Ji Kim, Young Eun Choi, Changsop Yang, Chang-Hyun Han, In-Hyuk Ha
Journal of Pain Research.2023; Volume 16: 2697. CrossRef - Domestic Clinical Research Trends of Shinbaro Pharmacopuncture: Scoping Review
Yeongmin Kim, Yunhee Han, Seungkwan Choi, Jungho Jo, Byeonghyeon Jeon, Hyeonjun Woo, Wonbae Ha, Junghan Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2023; 33(4): 125. CrossRef
- The effect of integrative Korean medicine treatment on symptomatic lumbar facet joint cysts: A case series



 First
First Prev
Prev


